Picture vs. Verbal Thought
Humans think in two ways: verbally and pictorially. Most everyone thinks in both modes, but each individual tends to specialize more in one area than another.
|
|
|
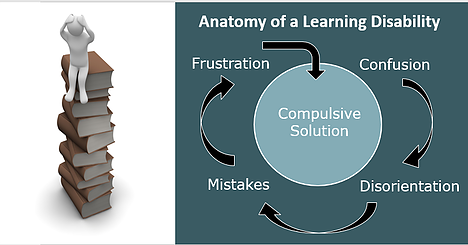
Anatomy of a Learning Disability
By Ronald D. Davis © 1985 - used with permission
- The individual encounters an unrecognized stimulus.
This could be a word (written or spoken), symbol, or object that is not recognized. - The lack of recognition causes a feeling of confusion.
- Confusion naturally and automatically stimulates or triggers disorientation.
The individual uses disorientation to mentally examine the stimulus in an attempt to bring about recognition and resolve the confusion. - Disorientation produces false sensory perceptions.
The different views and perceptions the individual is examining mentally are being registered in the brain as actual perceptions. - The disorientation and resulting false perceptions brings about the assimilation of incorrect data.
- The incorrect data causes the individual to make mistakes.
The individual cannot recognize the incorrect data as incorrect because it is registered in the brain as actual perception. - The mistakes cause emotional reactions.
No one likes to make mistakes. The individual is simply experiencing a human reaction. - Emotional reactions bring about a condition of frustration.
The frustration is a result of the cumulative effects of the mistakes and emotional reactions. - Compulsive solutions are created or adopted to solve the mistakes.
A solution will be a method of knowing something or a method of doing something. It will have worked at least once, and it will be compulsive. These solutions usually begin to appear around age eight or nine. Now instead of the confusion triggering a disorientation, it will trigger the compulsive solution.
Compulsive Solutions
Individuals adopt compulsive behaviors, patterns and mental tricks to reduce the mistakes and frustrations caused by disorientation.
Some common old solutions are:
|
DYSLEXICS:
1. Extreme concentration. 2. Memorizing rather than understanding. 3. Rereading over and over. 4. Sounding out each letter of every word. 5. Avoiding reading, writing or math tasks. 6. Getting others to read or write for them. |
ADD/ADHD:
1.Hanging around with the wrong crowds. 2. Becoming class clown. 3. Withdrawing from social situations. 4. Adopting the I don’t care attitude. 5. Extremely good at making up excuses. |